We analyzed quantitative real-time PCR qPCR assays on DNA extracted from these speci-mens to quantify nine organisms associated with vaginal health or disease. To examine whether these bacteria are also involved in BV in pregnant Japanese.
 Targeted Pcr For Detection Of Vaginal Bacteria Associated With Bacterial Vaginosis Journal Of Clinical Microbiology
Targeted Pcr For Detection Of Vaginal Bacteria Associated With Bacterial Vaginosis Journal Of Clinical Microbiology
NAATs detect one or more viral ribonucleic acid RNA genes and indicate a current infection or a recent infection but due to prolonged viral RNA detection are not always direct.
Bvab2 by rt pcr. Materials and Methods Patients and Specimen Collection From October 2009 to June 2010 163 unselected women attending the Department of Dermatovenereology Uppsala University Hospital Sweden for regular check-ups n90 or. The development of the polymerase chain reaction PCR for which Kary Mullis received the 1992 Novel Prize in Chemistry revolutionized molecular biology. Specific real-time PCR assays qPCR with the view of developing molecular criteria for the diagnosis of BV.
The t821q22q22 translocation results in constant expression of AML1ETO fusion mRNA which can be detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction RT-PCR. In our study both G. Clinical signs and Nugent scoring.
The use of quantitative diagnostic. Recent PCR-based studies suggested that BV is associated with complex vaginal bacterial communities including many newly recognized bacterial species in non-pregnant women. In con- PCR buffer II 2 mM magnesium chloride 08 mM deoxynucleoside triphosphate trast the combination of BVAB1 and BVAB2 or of BVAB2 mixture 1 unit AmpliTaq Gold DNA polymerase all from Applied Biosystems and BVAB3 did increase sensitivity for diagnosing BV to 02 M each of forward and reverse primers Table 1 and 1 l of template DNA.
This is achieved by monitoring the amplification. Jensenii utilizing vaginal fluid specimens algorithm reported as a. NAATs such as real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction RT-PCR are high-sensitivity high-specificity tests for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Gardnerellavaginalis Atopobiumvaginae BV-asso-ciated bacteria 2 BVAB2 an uncultured member of the order Clostridiales Megasphaeraphylotype 1 or 2 Lactobacillusiners. The quantitative t821 assay can be used not only to diagnose AML but also to serially monitor patients evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and predict early relapse. Real time RTPCR is a nuclear-derived method for detecting the presence of specific genetic material in any pathogen including a virus.
The aim of this study was to determine the feasibility of detecting bacterial vaginosis BV-related organisms in stored genital tract specimens using real-time PCR. It is primarily used to measure the amount of a specific RNA. We evaluated a quantitative real-time PCR qPCR assay to detect and quantify individual BV-associated bacterial communities.
We used eight taxon-directed real-time quantitative PCR qPCR assays targeting both easily cultivated vaginal bacteria Gardnerella vaginalis and Lactobacillus crispatus and fastidious bacteria BVAB1 BVAB2 BVAB3 LeptotrichiaSneathia Atopobium and Megasphaera-like species to measure levels of vaginal bacteria as reflected by bacterial. Vaginae were detected by real-time PCR in 100 of the BV patients but these bacteria were also detected in 78 and 63 of subjects without BV respectively confirming that the qualitative detection of these species had very low specificity 22 and 37 respectively. BVAB2 was detected in 514 357 samples.
Bacterial vaginosis BV the etiology of which is still uncertain increases the risk of preterm birth. Vaginal swabs were tested with PCR assays for Gardnerella vaginalis Atopobium vaginae BV associated bacterium type 2 BVAB2 and Megaspheara type 1 MS1. The best combination of PCR results for diagnosing BV arose from detection of either BVAB2 or Megasphaera phylotype 1 which produced a diagnostic sensitivity of 988 and a specificity of 885 in the combined subject cohort compared to the Amsel criteria for BV.
Infectious disease bacterial vaginosis and vaginitis quantitative real-time amplification of DNA markers for Gardnerella vaginalis Atopobium vaginae Megasphaera Type 1 Bacterial Vaginosis Associated Bacteria-2 BVAB-2 and Lactobacillus species L. Frozen cervicovaginal lavage CVL samples from 21 women were analyzed by real-time PCR for the numbers of Mycoplasma hominis Gardnerella vaginalis and lactobacilli. At around the time that prize was awarded research was being carried out by Russel Higuchi which led to the discovery that PCR can be monitored using fluorescent probes facilitating quantitative real-time PCR qPCR.
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction RT-PCR is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chain reaction PCR. Vaginal swabs from 247 South Af. Whole bacterial community analysis was performed by fluorescent Terminal Restriction Fragment Length polymorphism TRFLP of 16S-rDNA.
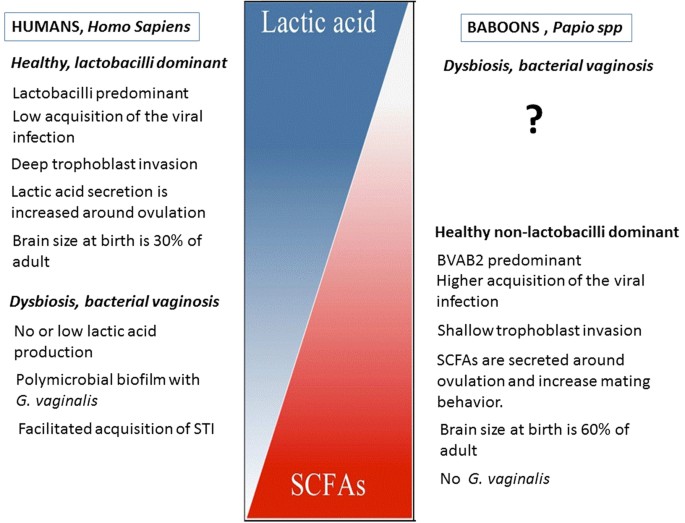
Diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis BV in resource-poor settings relies on semiquantitative microscopy algorithm such as the Nugent score NS. Originally the method used radioactive isotope markers to detect targeted genetic materials but subsequent refining has led to the replacement of isotopic labelling with special markers most frequently fluorescent dyes. The differences in the vaginal milieu between NHP and humans might be the factor associated with human-specific pattern of placental development and.
We analyzed quantitative real-time PCR qPCR assays on DNA extracted from these specimens to quantify nine organisms associated with vaginal health or diseaseGardnerella vaginalisAtopobium vaginae BV-associated bacteria 2 BVAB2 an uncultured member of the.

