The advantage of sequencing the whole exome is that the data can be re-analysed at a later date to include newly identified disease genes. Whole exome sequencing WES is a method of analyzing the protein coding regions also called the exome which comprise 1-2 of the entire genome.
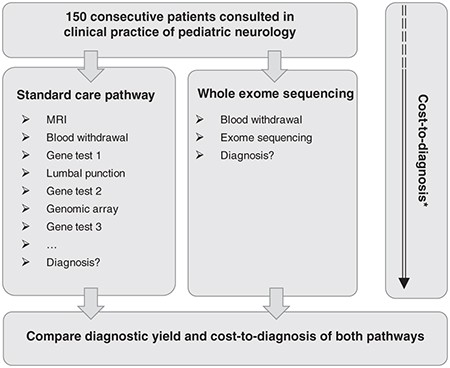 A Clinical Utility Study Of Exome Sequencing Versus Conventional Genetic Testing In Pediatric Neurology Genetics In Medicine
A Clinical Utility Study Of Exome Sequencing Versus Conventional Genetic Testing In Pediatric Neurology Genetics In Medicine
Exome sequencing also known as Whole exome sequencing WES is a genomic technique for sequencing all of the protein-coding regions of genes in a genome known as the exome.

Whole exome sequencing test. The format is GTR000000011 with a leading prefix GTR followed by 8 digits a period then 1 or more digits representing the version. In current study we evaluated the possibility of profiling both disease-causing SNPsIndels and CNVs in a single test based on WES in EEs. The purpose of whole exome sequencing is to try to find a genetic cause of your or your childs signs and symptoms.
Next-Generation Whole Exome Sequencing WES Test Details. WHOLE EXOME SEQUENCING WES test DESCRIPTION. The infants diagnosed with EEs were enrolled.
What is Whole-Exome Sequencing. What is Whole Exome Sequencing. This test is performed by Next Generation Sequencing.
The human genome comprises 3 billion base pairs. Exome are sequenced using next-generation sequencing technologies. In WES protein-coding regions of all genes 20000 of the human genome ie.
Together all the exons in a genome are known as the exome and the method of sequencing them is known as whole exome sequencing. This test includes whole exome sequencing of the Duo Proband patient of interest plus one first-degree relative usually one of the biological parent or Trio Proband patient of interest plus two first-degree relatives usually the biological parents using next generation sequencing methods targeted to the 20000 nuclear genes. Whole exome sequencing WES identifies changes in a patients DNA by focusing on the most informative regions of the genome the exome.
This is important as more than 50 of patients with genetic diseases are not given a specific diagnosis even after repeat clinical examinations and tests. This method allows variations in the protein-coding region of any gene to be identified rather than in only a select few genes. For certain patients the combination of symptoms does not allow the clinician to pinpoint a potential diagnosis.
Whole exome sequencing WES is widely adopted in clinical and research settings. The trio whole exome sequencing test uses an inheritance based gene agnostic approach. With the ability to screen all genes WES.
Yet only 12 code for protein the exome. Because WES looks at more genes than most genetic tests it may find a genetic cause for your or your childs signs and symptoms. The human exome represents less than 2 of the genome but contains about 85 of known disease-related variants making this method a cost-effective alternative to whole-genome sequencing.
WES is one of the most extensive genetic tests available. These pieces called exons are thought to make up 1 percent of a persons genome. GTR Test ID Help Each Test is a specific orderable test from a particular laboratory and is assigned a unique GTR accession number.
The WES test sequences and analyses 214405 exons dispersed throughout the genome. The human exome consists of approximately 180000 exons which constitutes about 1-2 of the human genome. However one of the practical concerns is the potential false negatives due to incomplete breadth and depth of coverage for several exons in clinically implicated genes.
When a laboratory updates a registered test a new version number. In some cases a targeted gene panel testing may be a dependable option to ascertain true negatives for genomic. The PGxome assesses almost all genes from the human genome including coding regions and adjacent introns.
Whole Exome Sequencing. This test is an appropriate choice for health care providers who are looking for an urgent genetic diagnosis. Whole exome sequencing WES is a robust and one of the most comprehensive genetic tests to identify the disease-causing changes in a large variety of genetic disorders.
Patients without molecular diagnosis who have exhausted currently available genetic testing Patients with a long differential diagnosis or genetically very heterogeneous disorder. Our WES test will also reliably detect CNVs of 3 exons or greater as well as additional common deletion events. WES is a cost-effective alternative to Whole Genome Sequencing.
Most people who have WES have already had some genetic testing. Whole exome sequencing WES is widely applied to detect SNVsIndels but the bioinformatics approach for detecting CNVs maybe limited or powerless. This test involves sequencing of the whole exome with enhanced coverage of known disease-causing genes as well as curated deep-intronic variants.
Whole exome sequencing is a commonly used next-generation sequencing NGS procedure which involves the sequencing of protein-coding regions of the genome. PGxome is PreventionGenetics whole exome sequencing WES test.
 Whole Exome Sequencing An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Whole Exome Sequencing An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Reliability Of Whole Exome Sequencing For Assessing Intratumor Genetic Heterogeneity Biorxiv
Reliability Of Whole Exome Sequencing For Assessing Intratumor Genetic Heterogeneity Biorxiv
 Impact Of Next Generation Whole Exome Sequencing In Molecular Diagnostics Sciencedirect
Impact Of Next Generation Whole Exome Sequencing In Molecular Diagnostics Sciencedirect
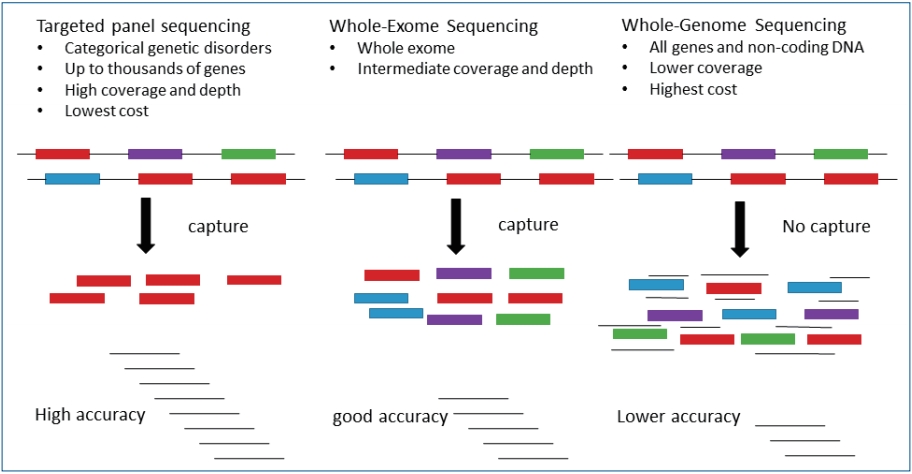 Genetic Tests By Next Generation Sequencing In Children With Developmental Delay And Or Intellectual Disability
Genetic Tests By Next Generation Sequencing In Children With Developmental Delay And Or Intellectual Disability
 Whole Exome Sequencing In The Evaluation Of Fetal Structural Anomalies A Prospective Cohort Study The Lancet
Whole Exome Sequencing In The Evaluation Of Fetal Structural Anomalies A Prospective Cohort Study The Lancet
 What Is Clinical Exome Sequencing Dna Labs India
What Is Clinical Exome Sequencing Dna Labs India
 Reliability Of Whole Exome Sequencing For Assessing Intratumor Genetic Heterogeneity Sciencedirect
Reliability Of Whole Exome Sequencing For Assessing Intratumor Genetic Heterogeneity Sciencedirect
 Patient And Family Guide Whole Exome Sequencing
Patient And Family Guide Whole Exome Sequencing
 Overview Of Whole Exome Sequencing Pipeline Snv Single Nucleotide Download Scientific Diagram
Overview Of Whole Exome Sequencing Pipeline Snv Single Nucleotide Download Scientific Diagram
 Overview Of Whole Exome Sequencing Pipeline Snv Single Nucleotide Download Scientific Diagram
Overview Of Whole Exome Sequencing Pipeline Snv Single Nucleotide Download Scientific Diagram





No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.